
Sqlite order by full#
This can be very useful if you are joining more than one table instead of repeating the full table name in the query, you can give each table a short alias name. This will give you all the columns in the table Students: For example, you can do this: SELECT s.* FROM Students AS s You can also give tables aliases, not just columns. The alias won’t change the column name it will just change the display name in the SELECT clause.Īlso, note that, the keyword “AS” is optional, you can put the alias name without it, something like this: SELECT StudentName 'Student Name' FROM Students Īnd it will give you the exact same output as the previous query: Note that, the column name still “ StudentName“ the column StudentName is still the same, it doesn’t change by the alias. This will give you the students’ names with the name “Student Name” instead of “StudentName” like this: The column aliases are specified using the keyword “AS”.įor example, if you want to select the StudentName column to be returned with “Student Name” instead of “StudentName” you can give it an alias like this: SELECT StudentName AS 'Student Name' FROM Students

The alias is a new name for the column that lets you select the column with a new name. It is a virtual column, created in the query for displaying the results and it won’t be created on the table. Note that, this new column Country is not actually a new column added to the table.
Sqlite order by plus#
This will give you all the students’ columns, plus a new column “Country” like this: For example, if you want to select all the students from Students table, with a new column called a country which contains the value “USA”, you can do this: SELECT *, 'USA' AS Country FROM Students This can be handy in some situations where you have to select a constant value for all the returned rows.

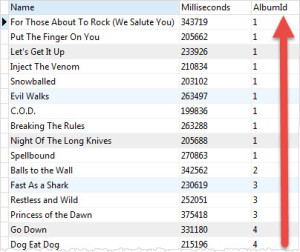
Note that, for all the following examples, you have to run the sqlite3.exe and open a connection to the sample database as flowing: In the from clause, you can specify one or more table or subquery to select the data from, as we will see later on the tutorials. The FROM clause is used to specify where do you want to select data. But before the select clause, let’s see from where we can select data using the FROM clause. In the SELECT clause, you state what to select. The SELECT clause is the main statement you use to query an SQLite database.
Sqlite order by how to#
To write SQL queries in an SQLite database, you have to know how the SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and LIMIT clauses work and how to use them.ĭuring this tutorial, you will learn how to use these clauses and how to write SQLite clauses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
